From Bitcoin to Blockchain to NFTs
If you're confused about this whole "web3" world and would like to separate fact from fiction, you're in the right place.
You’ve asked great questions, and great questions take time to answer.
Forgive me -
He who knows does not speak, and he who speaks does not know.
Tao Te Ching
The Louis Vuitton of Jamaica
What is the purpose of blockchain?
Let's say that you wanted to be the next Louis Vuitton of Jamaica.
You do your research, pour over countless designs with change after change after change, finalize the patterns, buy the fabric...wait, how would you buy the fabric?
Well, you'd find a place to buy the fabric, then hunt and hunt and hunt for the fabric that would make your design shine, and go to the checkout, and pay for the fabric...wait, how would you pay for the fabric?
Back in the day, depending on the fabric you chose, you might exchange the fabric for a maga goat. In modern times, you'd tap your credit card on the point-of-sale terminal and the money would be taken from your credit card account and transferred to Fabricland...Fabricland!
Without the credit card company, you couldn't pay for the fabric, let alone pay Jamaica-Z to wear your one-of-a-kind jacket at his next concert in US.
As you can see, the success or failure of your clothing line is your ability to engage in transactions. Every step of the way is lined with transactions. Whenever a startup pitches for funding, they're essentially promising that their company will be a future source of transactions.
When the US won the two world wars, they won the ability to influence the world's transactions. They influenced the transaction world by ensuring that oil was transacted in US dollars. Oil is the most important part of an economy, no matter what clean expert gurus will tell you.
For the past 80 years, most of the world's transactions have involved the US dollar. In the near future, countries in Europe and Southeast Asia will begin paying for oil in Russian Rubles…but I digress.
The point is, transactions are the core of an economy. Every step of your company’s progress is lined with a series of successful transactions. If your ability to conduct transactions were to stop, your business would end.
But there’s one assumption we’re making…and it could be a deadly one.
The one assumption that we make when we buy fabric or pay Jamaican-Z’s management to wear our clothing in the next concert is that our money is going to remain valuable. When we buy the fabric at Fabricland, we make an implicit assumption that one dollar in our account means we can buy one dollar of fabric.
But what happens when the value of the dollar goes down? Maybe you don't get as much fabric as you used to. Or maybe you don't get as much oil as you used to. If your business runs on fabric and oil, the value of your money is going down, maybe you don't have enough material to become the next Louis Vuitton of Jamaica.
Now that you understand that transactions and their underlying currency determines how an economy runs, you’re now prepared to understand why Bitcoin was created and how blockchain fits into the whole picture.
Bitcoin vs. Blockchains vs. NFTs
Long story short, Bitcoin was created so that you could launch the Louis Vuitton of Jamaica buy buying fabric from FabricLand without a credit card company processing the transaction for you.
In this new world, the creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakomoto, proposed a solution whereby the Bitcoin network would replace credit cards companies- and for that matter, any financial intermediary - as the main processor of transactions, globally.
Let’s understand what it takes to process transactions. When it comes to processing transactions, credit card companies employ massive amounts of people who use technology to execute the complex transaction-keeping - aka Accounting - to process transactions and make sure nobody steals your money and ensure that the same dollar doesn’t get spent twice. Doing this is NOT easy.
The technology that enables Bitcoin to process transactions like credit card companies involved the creation of a technology is called blockchain. You’ve probably heard of Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, BSV, BCH; these are all blockchain-based ecosystems like Bitcoin that use blockchain technology to perform the most difficult part of their business: processing transactions. In fact, processing transactions is still so difficult that the Solana Ecosystem was down yesterday. What happens when a transaction processor goes down? Businesses die. That’s why credit card companies are trusted to handle this core function.
OK. We’re getting closer. You got this.
Let’s take this slowly.
What is Bitcoin? What is Bitcoin in relation to Blockchain? What is Bitcoin in relation to Blockchain in relation to NFTs?
Those are the questions we’re attempting to answer. Pioneers have arrows in their backs, so you’d be wise to understand what’s happening so that when prices rise and crash, you don’t freak out.
Starting From First Principles
Consider the first line from the Bitcoin white paper,
A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution.
Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System, Satoshi Nakomoto, 2009
From one dimension, Bitcoin is an ecosystem that involves people who own Bitcoin. The owners of Bitcoin can send Bitcoin to each other. If I believe Bitcoin is worth something, I might even sell you expensive fabric in exchange for you sending me Bitcoin. Now why on earth why would I accept Bitcoin in exchange for fabric instead of dollars? Maybe I believe that I can use that Bitcoin to send to someone else who will give me a house in exchange for my Bitcoin. And people have bought houses with Bitcoin.
But what is Bitcoin in relation to blockchain? Where does blockchain fit in?
Bitcoin is an ecosystem of people, processes, and technologies that process transactions globally. Blockchain is the fundamental technologically-driven process that processes transactions securely without the need for a financial intermediary.
To understand the purpose of a blockchain, you have to understand what a blockchain is. A blockchain is a chain of digital blocks. Once a digital block has been created, it cannot be deleted; and that’s why accountants are so interested in it. What’s the value of a system whose values can’t be deleted?
The blockchain is powered by computers which act like calculators. These computers calculate one block of transactions at a time. The cool thing about blockchain is that you can have computers set up all around the world, processing transactions.
So, the purpose of blockchain was to enable the Bitcoin network to process transactions without fraud. Got it.
Bitcoin vs. Blockchains vs. NFTs
But where do NFTs fit in? How are NFTs different from Bitcoin and Blockchain? Let’s understand how everything fits together before defnining NFTs so you get the mind map of what’s going on.
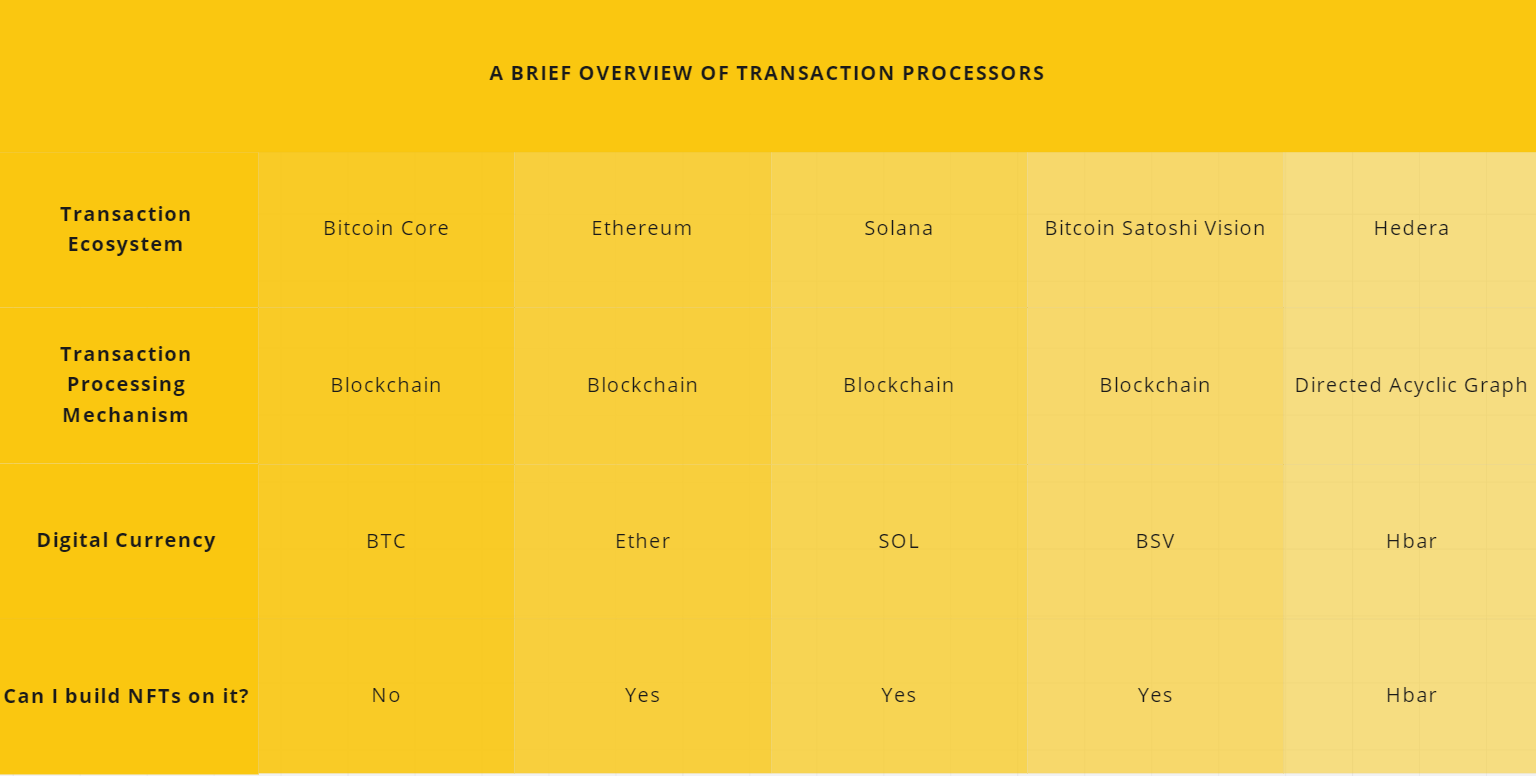
There are three major forms of Bitcoin - BTC, BCH, and BSV.
Bitcoin Core is an ecosystem that processes transactions using blockchain technology. The digital currency exchanged in the Bitcoin Ecosystem is called BTC.
Bitcoin Cash is an ecosystem that processes transactions. The technology used to process those transactions is called blockchain. The digital currency exchanged in the Bitcoin Ecosystem is called BCH.
Ethereum is an ecosystem that processes transactions. The technology used to process transactions in Ethereum is called blockchain. The digital currency exchanged in the Ethereum ecosystem is called Ether. NFTs can be created in the Ethereum ecosystem. NFTs created on Ethereum are priced in Ether.
Solana is an ecosystem that processes transactions. The technology used to process those transactions is called blockchain The digital currency exchanged in the Solana ecosystem is called SOL. NFTs can be created in the Solana Ecosystem. NFTs created in the Solana Ecosystem are priced in SOL.
Bitcoin SatoshiVision is an ecosystem that processes transactions. The technology used to process those transactions is called blockchain. The digital currency exchanged in the BSV ecosystem is called BSV. The BSV ecosystem can be used to create NFTs. NFTs created in the BSV ecosystem are priced in BSV. BSV was created because Satoshi Nakomoto aka Craig Wright got upset when other members of the original Bitcoin community wanted to change how the rules worked.
So where do NFTs fit in?
NFTs are digital objects with a unique signature.
Two Wills make Jada upset. How do you know if someone forged your will and created a new one and named themselves the beneficiary of your estate? Well, you could create a will as an NFT - thereby making a will a digital object with a unique digital signature.
NFTs are digital objects with a unique signature that you can create, buy and sell using transaction ecosystems like Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, and BSV.
Because people believe that Ether, Sol, Poly and BSV have varying amounts of value, when they see someone buying an NFT for $1,000.000.00 of ether, it turns heads. Now, the danger here is obvious - money laundering and price fetishism.
If I make a product available, and buy it from myself at $1,000.000.00, does that mean it’s worth a million dollars? Nope, but again, to the outside world, a monkey worth a million grabs headlines. Always remember that price is determined at the time of exchange; as the old adage goes, yesterday’s price is not today’s price.
Blockchains like Ethereum and Solana and BSV all have the feature of creating, hosting, and selling digital objects with a unique signature known as NFTs. NFTs are digital objects with a unique signature.
Today, people are excited about NFTs because they believe that anything in the physical world where there only needs to be one of that thing - from the Mona Lisa to a recording contract to a will- could be processed and have their uniqueness protected and exchanged through blockchains in the form of NFTs. I’m not sure how much you know about the art scene, but art is a great way to invest when equities are falling precipitously.
How are NFTs valued?
NFTs are priced in the currency of the ecosystem they were created in.
NFTs created in the Ethereum ecosystem are priced in Ether.
NFTs created in the Solana ecosystem are priced in SOL.
NFTs created in the BSV ecosystem are priced in BSV.
How NFTs can be transferred into objects like video, photos, and audio.
Decision 1: Do you want to create an NFT?
Decision 2: What will the NFT consist of? Videos, photos, or audio? Fancy code to do something incredible like represent a will?
Decision 3: Based on the kind of NFT you want to create, and based on what you can afford, you will then determine whether to create the NFT on Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, BSV, etc.
Decision 4: What is the process of uploading and selling and securing the NFT? What is the dominant Amazon of NFTs? The answer depends on how much money you have and which ecosystem your choose - Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, BSV, etc.
The Amazon of NFTs
For simplicity purposes, Opensea.io is the Amazon of NFTs. You can buy and sell NFTs created using Ethereum, Polygon AND Solana ecosystems on Opensea.io.
Creating an NFT is as simple or complex as you want. That said, the more code you add, the more you open yourself up to creative attacks.
How do I secure my NFTs?
Today, all of your digital currency and NFTs are held in wallets.
Digital currencies are best protected with a ledger hardware wallet available from Ledger.com. The only hardware wallet you should buy is from ledger.com
NFTs are stored in digital wallets like Metamask.io. Metamask.io can be tricky to protect because it’s a wallet that can be installed into your chrome web browser. People who plan on holding a lot of value in NFTs should consider specialized help. If you get hacked, it’ll already be too late.
To learn how to secure your NFTs against an attack, follow nftsareworthless on Twitter.
How do I trade my NFTs?
NFTs can be traded using your wallet. A popular digital currency and NFT wallet is Metamask.io.
How are NFTs mined?
NFTs are not mined. NFTs are created by paying a fee; the fee is based on the ecosystem you’ve chosen.
How do I create an NFT?
Go to Metamask.io and create a wallet.
Go to OpenSea.io and create an account. Your account will be tied to your Metamask wallet.
Create New Item.
Follow the instructions.
You don’t have to pay money to display your NFTs. Only when you’re ready to sell do you have to pay a network fee to get the ability to sell it. Kind of like shopify. You pay shopify so they can process your t-shirt sales.
Thanks, Jannette! And thanks to The Digital Mercenary Podcast team for their deep minds.